Use Case
For our selected use case Credit Applications we will train a model which should predict if credit payments will fail partialy or in total, based on some attributes of an individual person - describing the personal situation of the applicant. For the purpose this workshop the dataset has been simplified significantly by removing various attributes from the data set.
The simplication of the source data will have an impact with regards to prediction quality. We have decided to prioritize ease-of-use over prediction quality.
Prepare the Data Upload
Before we can load the data, create a table in the CREDIT schema for the overall data set. We will derive smaller datasets for the training and test phases from it in later steps:
CREATE TABLE "TRAIN" (
"SK_ID_CURR" BIGINT,
"TARGET" SMALLINT,
"CODE_GENDER" CHAR(5) DEFAULT 'U',
"FLAG_OWN_CAR" CHAR(5) DEFAULT '0',
"FLAG_OWN_REALTY" CHAR(5) DEFAULT '0',
"FLAG_MOBIL" CHAR(5) DEFAULT '0',
"FLAG_EMAIL" CHAR(5) DEFAULT '0',
"CNT_CHILDREN" SMALLINT,
"AMT_INCOME_TOTAL" DECIMAL(18,2),
"AMT_CREDIT" DECIMAL(18,2),
"AMT_ANNUITY" DECIMAL(18,2),
"AMT_GOODS_PRICE" DECIMAL(18,2),
"NAME_INCOME_TYPE" VARCHAR(64),
"NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE" VARCHAR(64),
"NAME_FAMILY_STATUS" VARCHAR(64),
"NAME_HOUSING_TYPE" VARCHAR(64),
DISTRIBUTE BY "SK_ID_CURR"
);
Load the dataset with the following command into the table TRAIN
IMPORT INTO TRAIN FROM CSV AT S3_EXASOL_DATA
FILE 'SOURCE_DATA/CREDIT_APPLICATION/CREDIT_DATA.csv'
This is the same connection we have used previously to load the RETAIL data for testing the Exasol database deployment.
Create the Datasets
First of all we create training sets of 50.000, 100.000 and 200.000 records in size. We will simply select the first n-th records from the TRAIN table:
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW TRAIN_50K AS (
SELECT *
FROM TRAIN
ORDER BY SK_ID_CURR ASC
LIMIT 50000
)
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW TRAIN_100K AS (
SELECT *
FROM TRAIN
ORDER BY SK_ID_CURR ASC
LIMIT 100000
)
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW TRAIN_200K AS (
SELECT *
FROM TRAIN
ORDER BY SK_ID_CURR ASC
LIMIT 200000
)
While we use the smallest training set for this workshop, feel free to experiment with larger data sets, too. Furthermore, we need to create at least one test set - for the purpose of this workshop we keep it small. Again, feel free to create bigger test sets. We are using the same strategy as before, but start from the end of the TRAIN table:
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW TEST_500 AS (
SELECT *
FROM TRAIN
ORDER BY SK_ID_CURR DESC
LIMIT 500
)
Train with SageMaker Autopilot
When you execute the SQL command to train a model, the Exasol SageMaker-Extension exports the specified table from the Exasol Database to your prevoiusly specified own AWS S3 bucket. This export operation is highly efficient, as it is performed in parallel. After that, the execution script calls Amazon SageMaker Autopilot, which automatically perform an end-to end machine learning development, to build a model. The following figure indicates this solution.
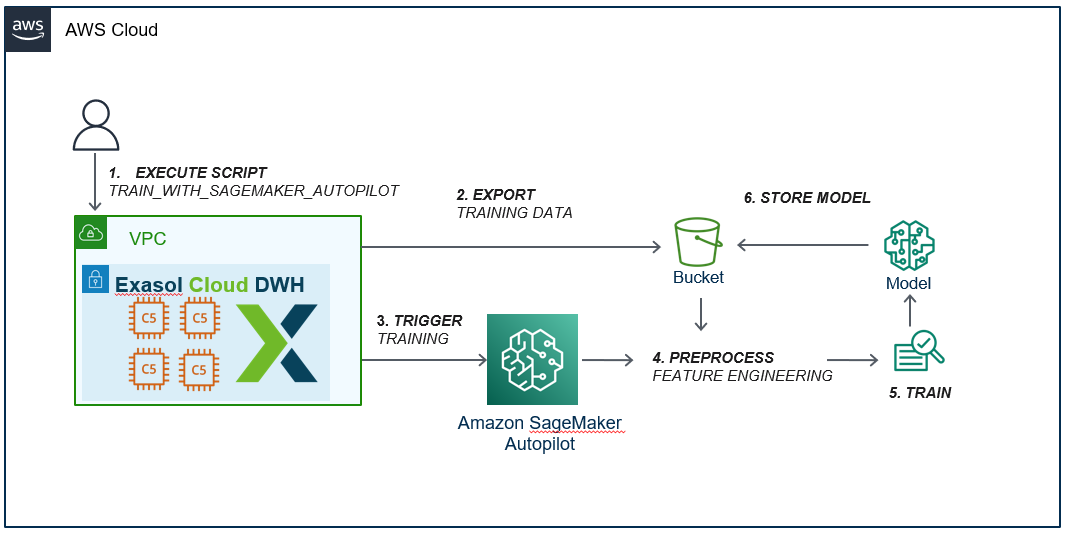
SME Training
The following command exports the TRAIN table in the CREDIT schema using the credentials stored in your previously created connection to your personal S3 bucket, into a given directory, and enables SageMaker Autopilot to start a job. Please note that the job name must be unique to the corresponding account, and it is case-insensitive. In addition, the maximum number of candidate models is in our case limited to 2 models by an optional parameter called max_candidates. On the other side, the other optional parameters that are not set in this sample SQL command such as problem_type, objective … etc. will be inferenced by Autopilot. For more information please check the User Guide at
SageMaker Autopilot Documentation
Execute the SQL command with DBVisualizer or the SQL client of your choice:
EXECUTE SCRIPT CREDIT."SME_TRAIN_WITH_SAGEMAKER_AUTOPILOT"(
'{
"job_name" : "CreditPredictor",
"aws_credentials_connection_name" : "<ConnectionName for your S3 bucket>",
"aws_region" : "<your desired AWS_REGION>",
"iam_sagemaker_role" : "sagemaker-role",
"s3_bucket_uri" : "<your own S3_BUCKET_URI>",
"s3_output_path" : "<your own <S3_OUTPUT_PATH>",
"input_schema_name" : "CREDIT",
"input_table_or_view_name" : "TRAIN_50K",
"target_attribute_name" : "TARGET",
"max_candidates" : 2
}');
This SQL command does not wait for the job to finish after calling Autopilot and completes its execution. The metadata information of the created Autopilot job is saved into the SME_METADATA_AUTOPILOT_JOBS table. You can query this table as follows:
SELECT *
FROM CREDIT."SME_METADATA_AUTOPILOT_JOBS";
The execution of the model training can take quite a moment / longer period, depending on the size of the dataset, but also varies by the chosen instance type, number of instances or number of model candidates. If the training process is failing, a message will be shown (see next step).
Poll Training Status
As mentioned in the above section, the training SQL script runs asynchronously. Therefore, you don’t have to wait for the training to finish. However, you can poll the status of the Autopilot training job with the polling SQL script provided by Exasol SageMaker-Extension. This SQL command takes the name of the job whose status will be queried, namely JOB_NAME, as input and returns the current status of the job. For more information please check the User Guide. You can execute the polling SQL command as follows:
EXECUTE SCRIPT CREDIT."SME_POLL_SAGEMAKER_AUTOPILOT_JOB_STATUS"(
'<JOB_NAME>',
'<AWS_CONNECTION_NAME>',
'<AWS_REGION>'
);
with a similar output like shown below:

Hereby, the JOB_STATUS can be one of the following states:
InProgress | Completed | Failed | Stopping | Stopped
while JOB_SECONDAY_STATUS may display one of the following states:
Starting | AnalyzingData | FeatureEngineering | ModelTuning | MaxCandidatesReached | Failed | Stopped | MaxAutoMLJobRuntimeReached | Stopping |
CandidateDefinitionsGenerated | GeneratingExplainabilityReport | Completed | ExplainabilityError | DeployingModel | ModelDeploymentError
AWS does not delete SageMaker jobs. If you run this training for multiple times, you have to change the job name, e.g. by adding a counter or version number to the job name to make the job name unique.
Deploy Sagemaker Endpoint
In order to perform predictions on a trained Autopilot model, one of the methods is to deploy the model to the real-time AWS SageMaker endpoint. You can use the deployment SQL command to create a real-time endpoint and deploy the best candidate model of the trained Autopilot jobs on it. The deployment SQL command additionally generates the prediction UDF script which is specific to the deployed endpoint so that you are able to perform real-time predictions. The following figure indicates this solution.
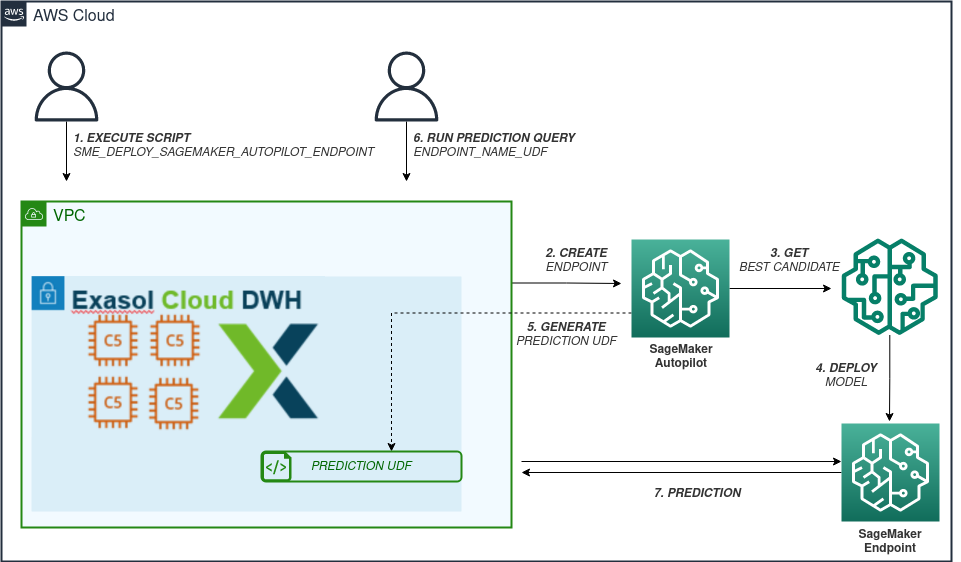
SME Training
The following deployment SQL command creates a SageMaker endpoint called ENDPOINT_NAME and deploys the best model of JOB_NAME on it. Please keep in mind, that the ENDPOINT_NAME is also the name of the UDF script generated for the prediction. Furthermore, you can specify a different database schema (DATABASE_PRED_SCHEMA) for the prediction UDF script to be installed than the one in which the scripts of the Exasol SageMaker-Extension project are deployed. For more information please check the User Guide. You can execute the deployment script with the defined variables as follows:
EXECUTE SCRIPT CREDIT."SME_DEPLOY_SAGEMAKER_AUTOPILOT_ENDPOINT"(
'<JobName>', // Unique Job_Name
'CreditPredictor', // The UDF function for the prediction
'CREDIT_PREDICTION', // Database Schema for storing the UDF predictor function
'ml.m5.large', // AWS instance type - do not change!
1,
'AWS_SME_CONNECTION', // The previously defined connection
'<your AWS region>' // AWS region you are working in
);
Remark: Keep the length of the JobName to 16 or less characters.
You should be able to retrieve the created UDF script for prediction, with the following SQL statement
SELECT SCRIPT_NAME,
SCRIPT_LANGUAGE
FROM SYS.EXA_ALL_SCRIPTS
WHERE SCRIPT_SCHEMA = 'CREDIT_PREDICTION'
AND SCRIPT_TYPE = 'UDF'
which shows you all defined Sagemaker Autopilot Endpoints:
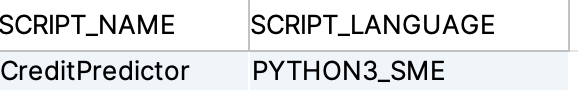
Use this information to check for existing endpoints you need to shutdown before ending your prediction work.
Predict via SageMaker Endpoint
The Exasol SageMaker-Extension generates a prediction UDF for each model, enabling you to perform prediction on the deployed endpoint. The name of the prediction script is the same as the name of the endpoint (ENDPOINT_NAME) specified when creating the endpoint.
The prediction UDF makes a real-time and synchronous call to the SageMaker endpoint. The prediction SQL command takes all the columns used while creating the model as inputs, appends the prediction result to these columns and the response is returned immediately. For more information, please check the User Guide. You can make prediction for this use case as follows:
WITH PREDICTION AS (
SELECT CREDIT_PREDICTION."CreditPredictor"(
A.SK_ID_CURR,
A.CODE_GENDER,
A.FLAG_OWN_CAR,
A.FLAG_OWN_REALTY,
A.FLAG_MOBIL,
A.FLAG_EMAIL,
A.CNT_CHILDREN,
A.AMT_INCOME_TOTAL,
A.AMT_CREDIT,
A.AMT_ANNUITY,
A.AMT_GOODS_PRICE,
A.NAME_INCOME_TYPE,
A.NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE,
A.NAME_FAMILY_STATUS,
A.NAME_HOUSING_TYPE)
FROM CREDIT.TEST_50 A
GROUP BY IPROC(), MOD(ROWNUM, 6)
)
SELECT P.*,
T.TARGET
FROM PREDICTION P JOIN CREDIT.TRAIN T ON P.SK_ID_CURR = T.SK_ID_CURR
You will get the following result set as an answer, obviously because of the limited training set the result is somewhat weak, We remove a substantial number of columns, but for this tutorial we gained ease-of-use. You may compare the results with the PREDICTIONS and TARGET column.
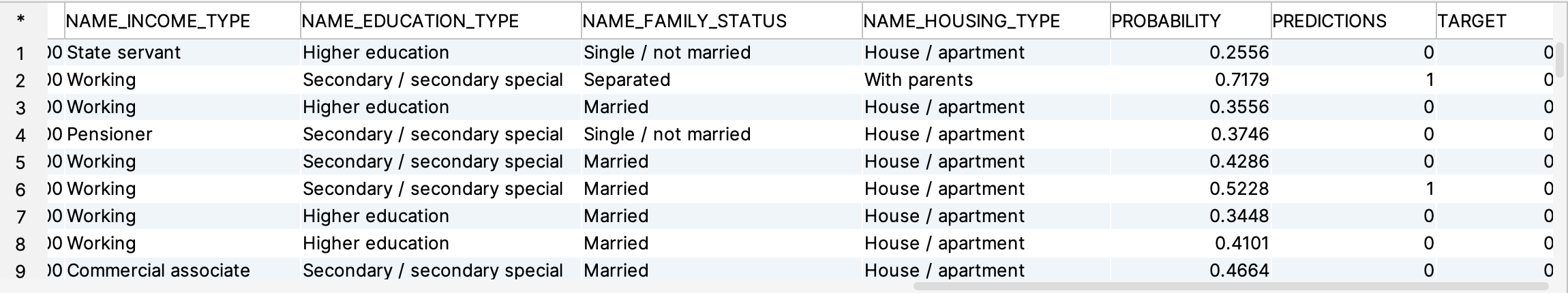
To enforce parallel execution of the SQL script with its so-called UDF function you need to add (as shown in the SQL statement) a GROUP BY iproc() clause which forces Exasol to distribute the execution of the function to all available cluster nodes.
Obviously, we are interested in the quality of the model we just trained. We can build a simple Confusion Matrix to see how good the model performs:
WITH PREDICTION AS (
SELECT CREDIT_PREDICTION."CP04"(
A.SK_ID_CURR,
A.CODE_GENDER,
A.FLAG_OWN_CAR,
A.FLAG_OWN_REALTY,
A.FLAG_MOBIL,
A.FLAG_EMAIL,
A.CNT_CHILDREN,
A.AMT_INCOME_TOTAL,
A.AMT_CREDIT,
A.AMT_ANNUITY,
A.AMT_GOODS_PRICE,
A.NAME_INCOME_TYPE,
A.NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE,
A.NAME_FAMILY_STATUS,
A.NAME_HOUSING_TYPE)
FROM CREDIT.TEST_1K A
GROUP BY IPROC(), MOD(ROWNUM, 6)
)
SELECT
T.TARGET AS Actual,
P.PREDICTIONS AS Predicted,
COUNT(1) AS Occurences
FROM PREDICTION P JOIN CREDIT.TRAIN T ON P.SK_ID_CURR = T.SK_ID_CURR
GROUP BY TARGET, PREDICTIONS
ORDER BY local.Actual, local.Predicted
As said before, our prediction model quality is not optimal due to the skipped attributes in our dataset:
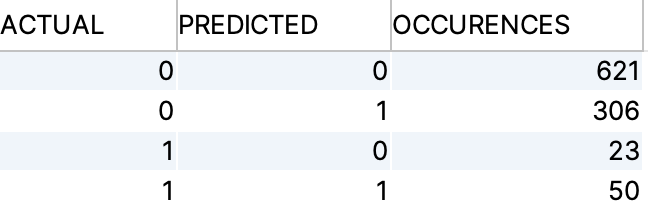
In this training run our model has a predicion quality of 67% - feel free to experiment with different training/test sets or the number of model candidates and see if the prediction quality improves.
Conclusion
In this part of the tutorial, we went through each steps of the installation and deployment of the Exasol SageMaker-Extension, and examined in detail how it works on a real-world problem.
The Exasol SageMaker-Extension provides a simple installation with the pre-packaged releases and perform a functional deployment with an easy-to-use CLI tool. The SQL commands which come with the deployment enable you to create the machine learning model of the table you want using the SageMaker Autopilot service and make your predictions.