AWS Athena & Exasol Virtual Schema
Exasol Virtual Schemas are an abstraction layer that makes external data sources accessible in our data analytics platform through regular SQL commands. The contents of the external data sources are mapped to virtual tables which look like and can be queried as any regular Exasol table.
After creating a virtual schema, you can use its tables in SQL queries and combine them with persistent tables stored in Exasol, or with any other virtual table from a different virtual schema. The Virtual Schema concept creates a type of logical view on top of several data sources that could be databases or other data services. It translates the Exasol SQL into the SQL of the remote database.
AWS Athena on the other hand is based under the hood on the Open-Source project Apache Presto. It is a distributed query engine for big data using the SQL query language. Athena provides a flexible way to analyze a large amount of data in Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) using standard SQL. Athena is serverless, so there is no infrastructure to set up or manage, and you can start analyzing data immediately.
AWS Athena requirements
Nevertheless, if we want to create an Athena table in the AWS Glue Data Catalog, we must first create a data source and specify a database for the table. Databases are used to organize metadata tables in the AWS Data Catalog. When you define a table in the Data Catalog, you add it to a database. A table can only belong to one database. Your database can contain tables that define data from a different data store. In our workshop we are going to use files in a Character Separated Value (CSV) format to demonstrate the idea behind Athena. For our purpose we use again the CITIES table from previous steps:
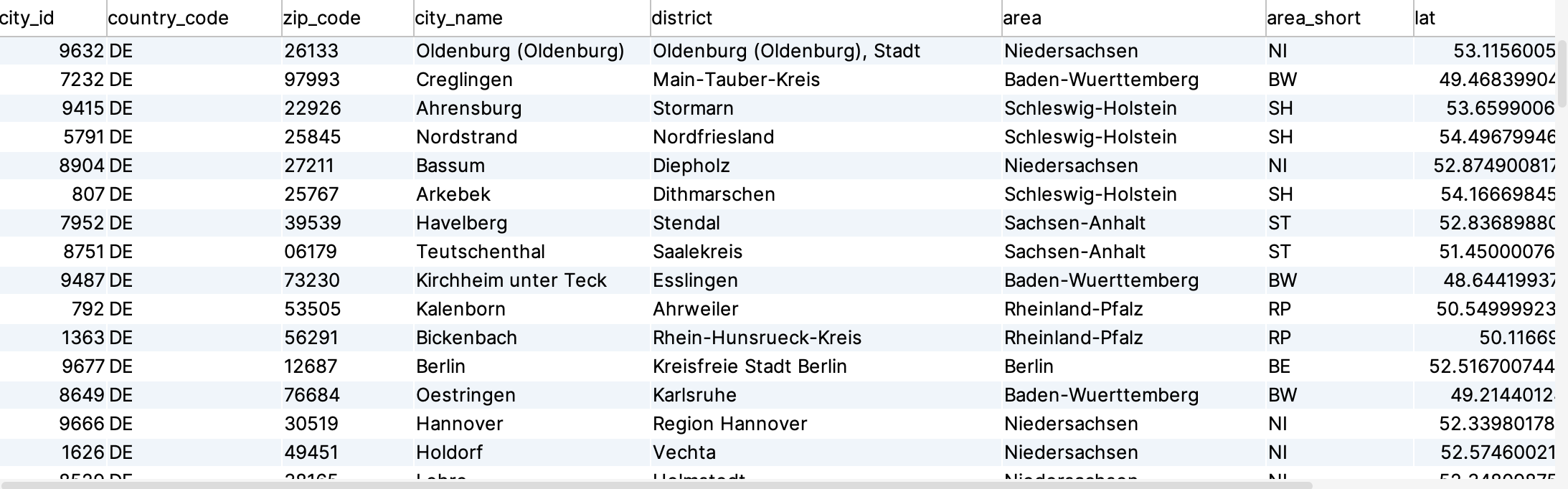
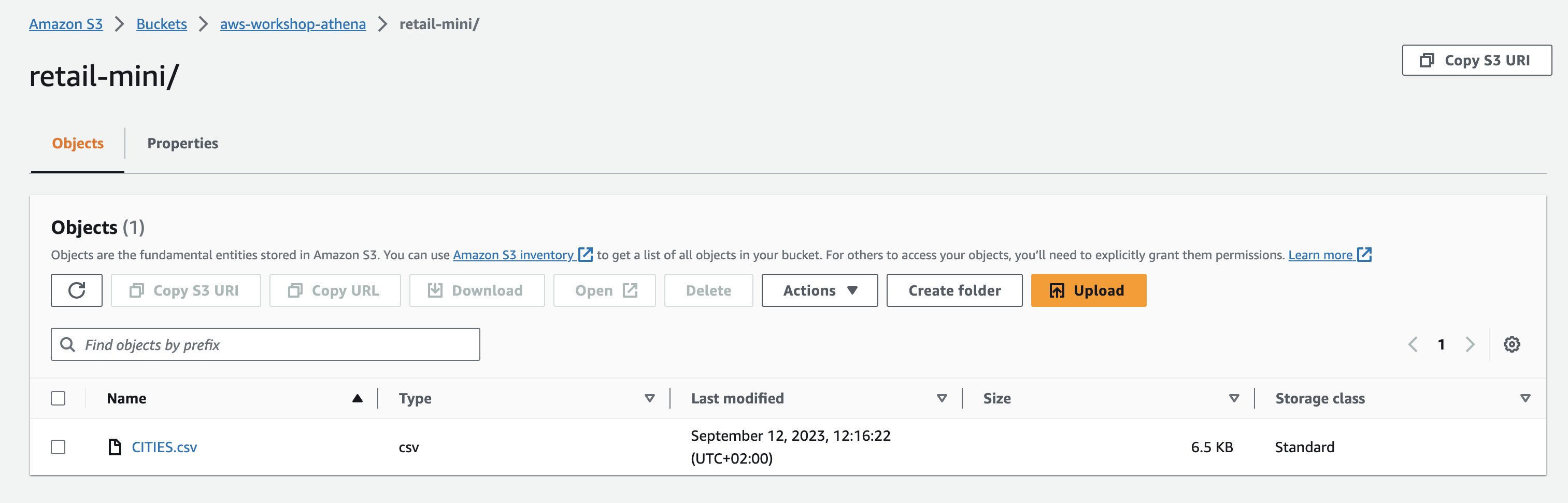
For the data catalog and the use of Athena therefore we need an S3 bucket and the underlying data.
To get started, sign into the AWS Management Console and open the S3 console. As a first step, generate an appropriate S3 bucket with a name chosen by you and upload the required CITIES.csv file from the
s3-aws-modernization-workshop
bucket.
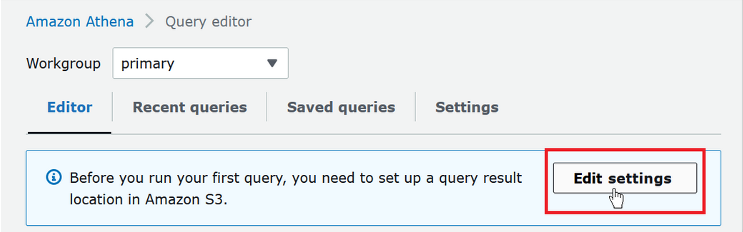
Amazon Athena automatically stores query results and metadata information for each query that runs in a query result location that you can specify in Amazon S3. If this is your first time to visit the Athena console in your current AWS Region, you need to set up a query result location in Amazon S3.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/athena/latest/ug/querying.html
After the required S3 buckets and data layer have been created, we can take care of the data catalog.